前言
常规的Out Box of Demo的食用方法TI官方给的已经很多了总结下来就是:
- 电脑装emupack(设备和电脑通过USB通信的驱动程序)
- Uniflash给设备烧录demo的预编译文件
- 使用demo_visualizer与设备通过UART通信并读取数据, 可视化数据
但是这样使用官方软件的方法并不适合我们做更进一步的处理, 比如目标识别, 跟踪等等信息处理. 所以我们要做的就是写一个脚本来替代demo_visualizer. 那为了完成这样一件事儿我们需要知道demo_visualizer的工作机制, 具体通信的方式, 数据格式等等细节.
在这篇博客中会有许多概念我们默认为读者已经提前了解了, 比如通用异步收发传输器(Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, UART), 基本的LFMCW雷达原理等. 如果有不清楚的概念搜索引擎搜索就可以得到需要的信息.
在这篇博客中我们将讲首先介绍out of box demo的数据传输方式以及格式, 之后会分别使用matlab和python给出一个例程, 这个例程可以读取雷达的数据还可以对数据进行可视化.
数据传输方式以及格式
数据传输方式
xWR设备使用UART与上位机通信,熟悉嵌入式的读者应该清楚从xWR SoC上的UART电平信号想通过USB传输一定需要一个转换电路将其转换为USB的差分信号, 同时还要能告诉USB host传输信号的源数据类型为UART. 那么这件工作是由谁来完成的呢, 对于xWR1642boost和xWR1843boost 是通过评估板上的一块XDS芯片完成的, 而对于xWR6843AoP, xWR6843ISK-ODS和xWR6843ISK 则是通过一块名为CP2015的UART bridge芯片完成的. 当你安装emupack这个驱动程序时, 其实你就安装了XDS的芯片驱动程序. 那CP2015的驱动程序呢? 由于CP2015是一块”烂大街”的芯片(使用极其广泛), 大多数Windows发行版在安装时就已经包含了这个驱动程序, 如果你的电脑不幸miss了CP2015的驱动程序, 通过网络你也可以很轻易的得到.
当你通过micro-USB的数据线将xWR评估板连接到你的电脑上时, 你会在设备管理器中看到检测到新插入的两个串行接口, 后面还会显示相应的COM标号:
- xWR1642boost和xWR1843boost会显示为
- xWR6843AoP, xWR6843ISK-ODS和xWR6843ISK会显示为

他们分别时CLI port和 Data port, CLI port传输你对demo程序的配置, 比如LFMCW雷达波形基础配置, 检测算法阈值的配置等等, 同时demo程序也会积极的与你交互, 告知你的配置格式数据是否合规. Data port传输经过雷达数据处理得到的检测点云数据, 芯片工作负载信息等等. 正是由于这两个串口不同的工作任务, 他们对信息传输的速度要求不同, CLI port工作在115200的波特率而Data port工作在926000的波特率. 当然这两个串口也是工作在全双工模式下的.
CLI port数据格式
CLI port是传输你对Demo程序的配置的端口, 配置信息的格式及相应的含义可以在1
/ti/mmwave_sdk_<ver>/docs/mmwave_sdk_user_guide.pdf
中的1
3.4 Configuration (.cfg) File Format
中找到
Data port数据格式
Data port的数据格式可以在1
> \ti\mmwave_sdk_<ver>\packages\ti\demo\xwr68xx\mmw\docs
中找到,如下图所示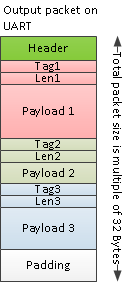
Data port数据输出格式是一个TLV格式的协议, 即就是每一个大的数据块(TLV)由 Tag, Length 和 Value 三个部分组成. 并且在 Data port 一次输出数据的过程中, 可能输出多个TLV, 这样在总的数据块头部, 需要一个总的Header数据段以告知该数据包TLV的数目以及这个Packet的长度(in bytes). 那么每个TLV传输的是什么数据呢? 比如检测的点云数据, 距离多普勒数据, 距离幅度的一维数据等等. 熟悉C语言的读者可以发现, 这样的多段线性的存储结构可以使用结构体来实现, 这也是TI 的官方Demo程序的做法. Packet 的header结构体叫 MmwDemo_output_message_header_t
1 | typedef struct MmwDemo_output_message_header_t |
每个结构体成员变量的含义可以在以下html文档中查看1
/ti/mmwave_sdk_02_01_00_04/packages/ti/demo/xwr16xx/mmw/docs/doxygen/html/struct_mmw_demo__output__message__header__t.html
仅仅通过变量的名称我们可以发现, Packet的header包含了SDK的版本, Packet的长度, mmWave Device的名称, Packet的编号, 检测点的个数以及TLV的个数. 那么之后就是要确定每个TLV的格式了, Demo 中给出了几种功能的TLV
- List of detected objects
- Range profile
- Noise floor profile
- Azimuth static heatmap
- Range/Doppler heatmap
- Stats information
每种TLV的功能可以参见如下文档的 Output information sent to host 部分1
/ti/mmwave_sdk_02_01_00_04/packages/ti/demo/xwr16xx/mmw/docs/doxygen/html/index.html
在这里着重要说明的是检测点云(List of detected objects)的输出格式, 也是我们需要重点需要从 Demo 中获得的数据
List of detected objects TLV 的数据结构如图
Tag和Length的结构体定义如下1
2
3
4
5typedef struct MmwDemo_output_message_tl_t
{
uint32_t type;
uint32_t length;
} MmwDemo_output_message_tl;
而List of detected objects TLV的第二个结构体包含了检测到的点的个数与坐标存储的格式(Q-format, 即定点数)1
2
3
4
5typedef struct MmwDemo_output_message_dataObjDescr_t
{
uint16_t numDetetedObj;
uint16_t xyzQFormat;
} MmwDemo_output_message_dataObjDescr;
在MmwDemo_output_message_dataObjDescr之后紧跟着numDetetedObj个检测的点云数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9typedef volatile struct MmwDemo_detectedObj_t
{
uint16_t rangeIdx;
int16_t dopplerIdx;
uint16_t peakVal;
int16_t x;
int16_t y;
int16_t z;
} MmwDemo_detectedObj;
相关代码(matlab)
打开传输串口
1 | function [CLI_sphandle,DATA_sphandle] = setupUART(CLIcomPortString,DATAcomPortString) |
CLI port配置数据
1 | % Carrier frequency GHz 60.25 |
读取CLI port配置数据
1 | function [configcmd] = readCfgFile(configFile) |
发送CLI port的配置数据
1 | function sendCfg(UART_sphandle,configcmd) |
读取Data port数据
1 | function [dataOk, frameNumber, detObj] = readAndParseData(DATA_sphandle) |
示例程序
1 | clear all; close all |
相关代码(Python)
依赖
在Python的代码中需要安装如下几个依赖:
- pyserial: 用于通过串口与设备进行通信
- numpy: 进行矩阵的操作和部分数学处理
- Pyqt, Pyqtgraph, OpenGL: 对数据进行可视化操作并显示
- sklearn: 聚类等操作
- pandas: 数据管理
代码
在这个代码中其实进行了DBscan聚类的处理, 感兴趣的读者可以多多尝试其他的信息处理方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364#
# File: 读取IWR6843处理得到的点云数据(3维)进行目标跟踪,同时调用openGL对点云进行显示
# Author: UESTC Yu Xuyao
# Email: yxy19991102@163.com
#
import serial
import time
import numpy as np
import pyqtgraph as pg
from pyqtgraph.Qt import QtGui
import pyqtgraph.opengl as gl
# from IWR.MOT3D import *
import numpy
from sklearn.cluster import dbscan
import pandas
# Change the configuration file named
configFileName = 'profile_iwr6843_ods_3d.cfg'
# configFileName = 'profile_3d.cfg'
CLIport = {}
Dataport = {}
byteBuffer = np.zeros(2 ** 15, dtype='uint8')
byteBufferLength = 0
testroot = []
confirmedroot = []
Z_k_prev = numpy.mat([])
cnt = 1
show = []
changdu = 5
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Function to configure the serial ports and send the data from
# the configuration file to the radar
def serialConfig(configFileName):
global CLIport
global Dataport
# Open the serial ports for the configuration and the data ports
# Raspberry pi
# CLIport = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0', 115200)
# Dataport = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM1', 921600)
# Windows
CLIport = serial.Serial('COM3', 115200)
Dataport = serial.Serial('COM4', 921600)
# CLIport = serial.Serial('COM22', 115200)
# Dataport = serial.Serial('COM21', 921600)
# Read the configuration file and send it to the board
config = [line.rstrip('\r\n') for line in open(configFileName)]
for i in config:
print(i)
if len(i)>0:
if i[0] != '%':
CLIport.write((i + '\n').encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
reply = CLIport.read(CLIport.in_waiting).decode()
print(reply)
return CLIport, Dataport
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Function to parse the data inside2 the configuration file
def parseConfigFile(configFileName):
configParameters = {} # Initialize an empty dictionary to store the configuration parameters
# Read the configuration file and send it to the board
config = [line.rstrip('\r\n') for line in open(configFileName)]
for i in config:
# Split the line
splitWords = i.split(" ")
# Hard code the number of antennas, change if other configuration is used
numRxAnt = 4
numTxAnt = 3
# Get the information about the profile configuration
if "profileCfg" in splitWords[0]:
startFreq = int(float(splitWords[2]))
idleTime = int(splitWords[3])
rampEndTime = float(splitWords[5])
freqSlopeConst = float(splitWords[8])
numAdcSamples = int(splitWords[10])
numAdcSamplesRoundTo2 = 1
while numAdcSamples > numAdcSamplesRoundTo2:
numAdcSamplesRoundTo2 = numAdcSamplesRoundTo2 * 2
digOutSampleRate = int(splitWords[11])
# Get the information about the frame configuration
elif "frameCfg" in splitWords[0]:
chirpStartIdx = int(splitWords[1])
chirpEndIdx = int(splitWords[2])
numLoops = int(splitWords[3])
numFrames = int(splitWords[4])
framePeriodicity = float(splitWords[5])
# Combine the read data to obtain the configuration parameters
numChirpsPerFrame = (chirpEndIdx - chirpStartIdx + 1) * numLoops
configParameters["numDopplerBins"] = numChirpsPerFrame / numTxAnt
configParameters["numRangeBins"] = numAdcSamplesRoundTo2
configParameters["rangeResolutionMeters"] = (3e8 * digOutSampleRate * 1e3) / (
2 * freqSlopeConst * 1e12 * numAdcSamples)
configParameters["rangeIdxToMeters"] = (3e8 * digOutSampleRate * 1e3) / (
2 * freqSlopeConst * 1e12 * configParameters["numRangeBins"])
configParameters["dopplerResolutionMps"] = 3e8 / (
2 * startFreq * 1e9 * (idleTime + rampEndTime) * 1e-6 * configParameters["numDopplerBins"] * numTxAnt)
configParameters["maxRange"] = (300 * 0.9 * digOutSampleRate) / (2 * freqSlopeConst * 1e3)
configParameters["maxVelocity"] = 3e8 / (4 * startFreq * 1e9 * (idleTime + rampEndTime) * 1e-6 * numTxAnt)
return configParameters
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Funtion to read and parse the incoming data
def readAndParseData68xx(Dataport, configParameters):
global byteBuffer, byteBufferLength
# Constants
OBJ_STRUCT_SIZE_BYTES = 12
BYTE_VEC_ACC_MAX_SIZE = 2 ** 15
MMWDEMO_UART_MSG_DETECTED_POINTS = 1
MMWDEMO_UART_MSG_RANGE_PROFILE = 2
maxBufferSize = 2 ** 15
tlvHeaderLengthInBytes = 8
pointLengthInBytes = 16
magicWord = [2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 8, 7]
# Initialize variables
magicOK = 0 # Checks if magic number has been read
dataOK = 0 # Checks if the data has been read correctly
frameNumber = 0
detObj = {}
readBuffer = Dataport.read(Dataport.in_waiting)
byteVec = np.frombuffer(readBuffer, dtype='uint8')
byteCount = len(byteVec)
# Check that the buffer is not full, and then add the data to the buffer
if (byteBufferLength + byteCount) < maxBufferSize:
byteBuffer[byteBufferLength:(byteBufferLength + byteCount)] = byteVec[0:byteCount]
byteBufferLength = byteBufferLength + byteCount
# Check that the buffer has some data
if byteBufferLength > 16:
# Check for all possible locations of the magic word
possibleLocs = np.where(byteBuffer == magicWord[0])[0]
# Confirm that is the beginning of the magic word and store the index in startIdx
startIdx = []
for loc in possibleLocs:
check = byteBuffer[loc:loc + 8]
if np.all(check == magicWord):
startIdx.append(loc)
# Check that startIdx is not empty
if startIdx:
# Remove the data before the first start index
if 0 < startIdx[0] < byteBufferLength:
byteBuffer[:byteBufferLength - startIdx[0]] = byteBuffer[startIdx[0]:byteBufferLength]
byteBuffer[byteBufferLength - startIdx[0]:] = np.zeros(len(byteBuffer[byteBufferLength - startIdx[0]:]),
dtype='uint8')
byteBufferLength = byteBufferLength - startIdx[0]
# Check that there have no errors with the byte buffer length
if byteBufferLength < 0:
byteBufferLength = 0
# Read the total packet length
totalPacketLen = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[12:12 + 4], byteorder='little')
# Check that all the packet has been read
if (byteBufferLength >= totalPacketLen) and (byteBufferLength != 0):
magicOK = 1
# If magicOK is equal to 1 then process the message
if magicOK:
# Initialize the pointer index
idX = 0
# Read the header
magicNumber = byteBuffer[idX:idX + 8]
idX += 8
version = format(int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little'), 'x')
idX += 4
totalPacketLen = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
platform = format(int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little'), 'x')
idX += 4
frameNumber = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
timeCpuCycles = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
numDetectedObj = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
numTLVs = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
subFrameNumber = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
# Read the TLV messages
for tlvIdx in range(numTLVs):
# Check the header of the TLV message
tlv_type = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
tlv_length = int.from_bytes(byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4], byteorder='little')
idX += 4
# Read the data depending on the TLV message
if tlv_type == MMWDEMO_UART_MSG_DETECTED_POINTS:
# Initialize the arrays
x = np.zeros(numDetectedObj, dtype=np.float32)
y = np.zeros(numDetectedObj, dtype=np.float32)
z = np.zeros(numDetectedObj, dtype=np.float32)
velocity = np.zeros(numDetectedObj, dtype=np.float32)
for objectNum in range(numDetectedObj):
# Read the data for each object
x[objectNum] = byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4].view(dtype=np.float32)
idX += 4
y[objectNum] = byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4].view(dtype=np.float32)
idX += 4
z[objectNum] = byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4].view(dtype=np.float32)
idX += 4
velocity[objectNum] = byteBuffer[idX:idX + 4].view(dtype=np.float32)
idX += 4
# Store the data in the detObj dictionary
detObj = {"numObj": numDetectedObj, "x": x, "y": y, "z": z, "velocity": velocity}
dataOK = 1
# Remove already processed data
if 0 < idX < byteBufferLength:
shiftSize = totalPacketLen
byteBuffer[:byteBufferLength - shiftSize] = byteBuffer[shiftSize:byteBufferLength]
byteBuffer[byteBufferLength - shiftSize:] = np.zeros(len(byteBuffer[byteBufferLength - shiftSize:]),
dtype='uint8')
byteBufferLength = byteBufferLength - shiftSize
# Check that there are no errors with the buffer length
if byteBufferLength < 0:
byteBufferLength = 0
return dataOK, frameNumber, detObj
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Funtion to update the data and display in the plot
def update():
dataOk = 0
global detObj, confirmedroot, testroot, Z_k_prev, GLScatterPlot
global show, cnt
x = []
y = []
z = []
mask = 1
# Read and parse the received data
dataOk, frameNumber, detObj = readAndParseData68xx(Dataport, configParameters)
if dataOk:
x = detObj["x"]
y = detObj["y"]
z = detObj["z"]
if len(x) != 0:
try:
core_samples, cluster_ids = dbscan(np.vstack((x, y, z)).T, eps=0.3, min_samples=5)
except:
# print(np.vstack((x, y, z)).T)
return dataOk
df = pandas.DataFrame(np.c_[np.vstack((x, y, z)).T, cluster_ids],
columns=['x', 'y', 'z', 'cluster_id'])
df = df[df.cluster_id != -1]
count = df['cluster_id'].value_counts()
x = []
y = []
z = []
if count.shape[0] >= 1:
for i in range(0, count.shape[0]):
df1 = df[df.cluster_id == i]
# mean = np.mean([df1['x'], df1['y'], df1['z']], 1)
x = numpy.hstack((x, df1['x'].values))
y = numpy.hstack((y, df1['y'].values))
z = numpy.hstack((z, df1['z'].values))
# Z_k = np.vstack((x, y, z)).T
# if cnt==1:
# show = Z_k
# cnt += 1
# elif cnt<changdu:
# show = numpy.vstack((show,Z_k))
# cnt+=1
# elif cnt==changdu:
# cnt = 1
# show = numpy.vstack((show, Z_k))
# GLScatterPlot.setData(pos=show)
Z_k = np.vstack((x, y, z)).T
GLScatterPlot.setData(pos=Z_k, color=(1., 1., 1., .9))
# confirmedroot, testroot, Z_k_prev = MOT(Z_k, Z_k_prev, confirmedroot, testroot)
# if len(confirmedroot) > 0:
# tmppos = confirmedroot[0].est[0:3, :].T.A
# for i in range(1,len(confirmedroot)):
# tmppos = numpy.vstack((tmppos,confirmedroot[i].est[0:3, :].T.A))
# LinePlot.setData(pos=tmppos)
# QtGui.QApplication.processEvents()
# else:
# LinePlot.setData(pos=np.array([100, 100, 100]))
# QtGui.QApplication.processEvents()
# ------------------------- MAIN -----------------------------------------
# Configurate the serial port
CLIport, Dataport = serialConfig(configFileName)
# Get the configuration parameters from the configuration file
configParameters = parseConfigFile(configFileName)
# START QtAPPfor the plot
app = QtGui.QApplication([])
app = pg.mkQApp()
view = gl.GLViewWidget()
view.show()
axis = gl.GLAxisItem()
axis.scale(10, 10, 10)
view.addItem(axis)
GLScatterPlot = gl.GLScatterPlotItem()
view.addItem(GLScatterPlot)
# Main loop
timer = pg.QtCore.QTimer()
timer.timeout.connect(update) # 定时调用plotData函数
timer.start(50) # 多少ms调用一次
app.exec_()